Adding Rows to Pandas DataFrame: A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on
In data analysis and machine learning projects, you often need to add new observations to a Pandas DataFrame. Whether you are dealing with survey data, sensor readings, or user behavior logs, you must be able to append new rows to an existing DataFrame efficiently. Pandas, a popular data manipulation library in Python, offers several methods to add rows to a DataFrame. In this tutorial, we will explore three of them: .loc, .append, and .concat. Let's dive in.
Want to quickly create Data Visualizations in Python?
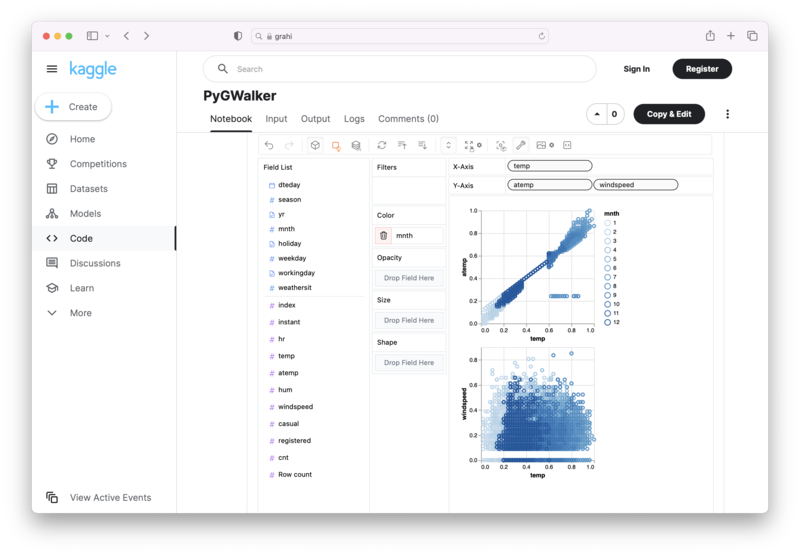
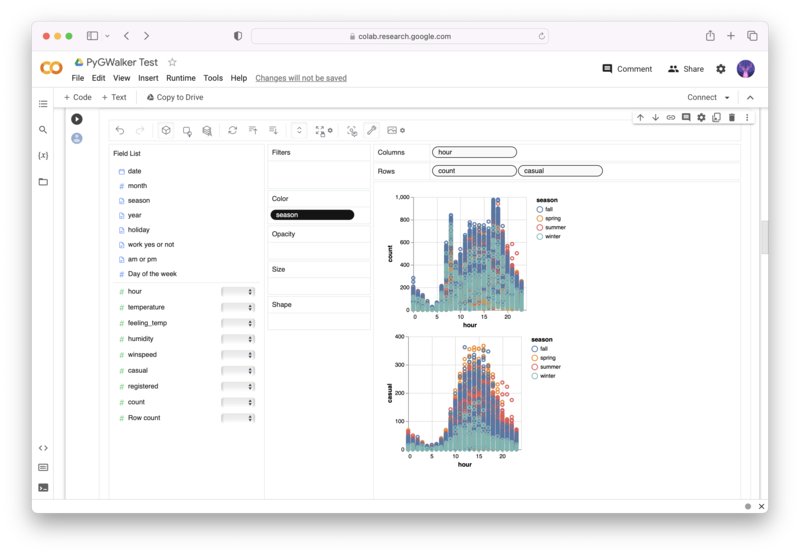
PyGWalker is an Open Source Python Project that can help speed up the data analysis and visualization workflow directly within a Jupyter Notebook-based environments.
PyGWalker (opens in a new tab) turns your Pandas Dataframe (or Polars Dataframe) into a visual UI where you can drag and drop variables to create graphs with ease. Simply use the following code:
pip install pygwalker
import pygwalker as pyg
gwalker = pyg.walk(df)You can run PyGWalker right now with these online notebooks:
And, don't forget to give us a ⭐️ on GitHub!
Adding a Row using .loc Method
The .loc method in Pandas allows you to select a subset of a DataFrame based on its labels. You can also use it to add a new row to the DataFrame. Here's how:
import pandas as pd
# creating a sample dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['John', 'Sara', 'Tim'],
'Age': [25, 34, 41],
'City': ['New York', 'London', 'Paris']
})
# adding a new row using .loc
df.loc[3] = ['Anna', 29, 'Berlin']
print(df)In the code above, we first create a DataFrame df with three rows and three columns. Then, we use the .loc method and specify a row index of 3. Finally, we provide a list of values for the new row.
Output:
Name Age City
0 John 25 New York
1 Sara 34 London
2 Tim 41 Paris
3 Anna 29 BerlinNote that the row index of the new row is 3, which means it will be added after the last row of the DataFrame. You can also use .loc to insert a row at a specific location by specifying the row label. For example, to insert a new row after the second row of the DataFrame, you can do:
# inserting a new row after the second row
df.loc[2.5] = ['Peter', 37, 'Los Angeles']
print(df)Output:
Name Age City
0 John 25 New York
1 Sara 34 London
2 Tim 41 Paris
2.5 Peter 37 Los Angeles
3 Anna 29 BerlinHere, we insert the new row after the label 2 by using a label of 2.5. Pandas automatically reorders the row labels to keep them in ascending order.
Adding a Row using .append Method
The .append method in Pandas allows you to combine two DataFrames vertically. You can use it to add a new row to a DataFrame by passing a DataFrame with a single row to the .append method. Here's an example:
# creating a new row as a dataframe
new_row = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Julia'],
'Age': [31],
'City': ['Tokyo']
})
# using .append to add the new row
df = df.append(new_row, ignore_index=True)
print(df)Output:
Name Age City
0 John 25 New York
1 Sara 34 London
2 Tim 41 Paris
3 Anna 29 Berlin
4 Julia 31 TokyoIn the code above, we first create a new DataFrame new_row with a single row of data. Then, we use the .append method and pass new_row as the argument. The ignore_index=True parameter tells Pandas to reindex the DataFrame from 0 to 4.
Adding Multiple Rows using .concat Method
The .concat method in Pandas allows you to concatenate two DataFrames along a specified axis. You can use it to add multiple rows to a DataFrame by passing a list of DataFrames to the .concat method. Here's how you can add two new rows to the DataFrame df using .concat.
# creating two new rows as dataframes
new_rows = [pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Maria', 'Adam'],
'Age': [27, 45],
'City': ['Sydney', 'Toronto']}),
]
# using .concat to add the new rows
df = pd.concat([df] + new_rows, ignore_index=True)
print(df)Output:
Name Age City
0 John 25 New York
1 Sara 34 London
2 Tim 41 Paris
3 Anna 29 Berlin
4 Maria 27 Sydney
5 Adam 45 TorontoIn the code above, we first create two new DataFrames new_rows. Then, we pass them as a list to the .concat method along with df. The ignore_index=True parameter reorders the index from 0 to 5.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we explored three different methods to add new rows to a Pandas DataFrame in Python: .loc, .append, and .concat. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on the situation. The .loc method is useful when you want to add a single row at a specific location. The .append method is a simple way to add a single row to the end of a DataFrame. The .concat method is ideal when you want to add multiple rows at once. Knowing these methods will help you manipulate DataFrames efficiently and effectively in your data analysis and machine learning projects. Happy coding!