Master Python Booleans: Understanding and Using Truth Values
Published on
Python is a versatile and powerful programming language, and one of the core elements in Python programming is the Boolean data type. Understanding and effectively utilizing Booleans can make your code more efficient and readable. In this essay, we'll delve into the world of Python Booleans, exploring topics like Boolean operators, comparison operators, and more.
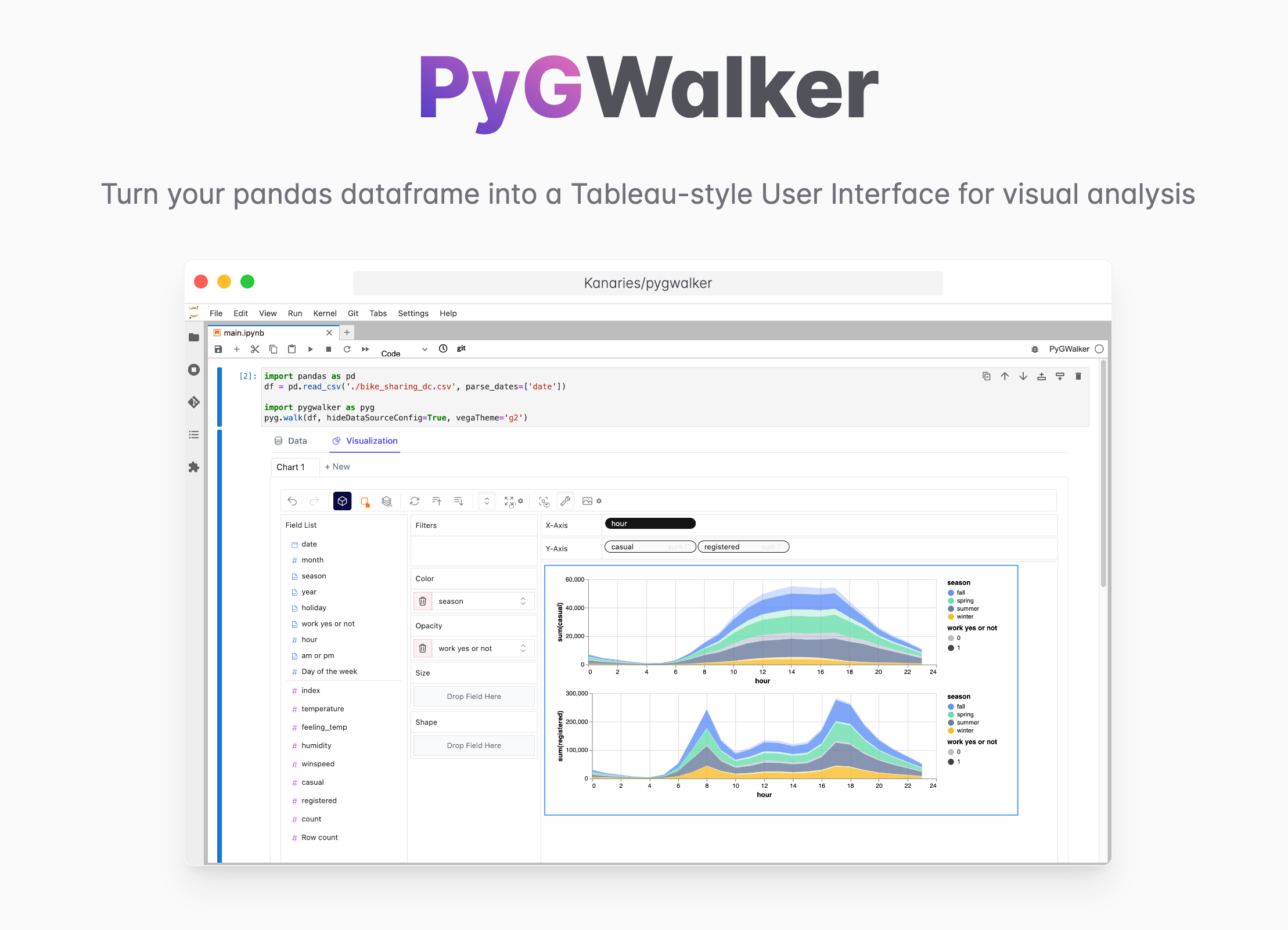
Want to quickly create Data Visualization from Python Pandas Dataframe with No code?
PyGWalker is a Python library for Exploratory Data Analysis with Visualization. PyGWalker (opens in a new tab) can simplify your Jupyter Notebook data analysis and data visualization workflow, by turning your pandas dataframe (and polars dataframe) into a Tableau-style User Interface for visual exploration.
What is the Python Boolean Type?
In the Python programming language, the Boolean data type represents two truth values: True and False. These values play a crucial role in controlling the flow of Python code and in writing efficient code. Booleans are a fundamental part of programming concepts and are used in various contexts, such as conditional statements and loops.
How do Boolean Operators Work in Python?
Boolean operators in Python are used to combine or manipulate Boolean values to form more complex expressions. The three primary Boolean operators are and, or, and not.
and: This operator returnsTrueif both operands areTrue, otherwise, it returnsFalse.or: This operator returnsTrueif either of the operands isTrue, otherwise, it returnsFalse.not: This operator negates the Boolean value it is applied to, returningFalseif the operand isTrue, andTrueif the operand isFalse.
You can find more examples and tutorials on Boolean expressions in Python to better understand how these operators work.
Can Boolean Values be Converted to Other Types?
Yes, Boolean values can be converted to other data types in Python. When converting Booleans to integers, True becomes 1, and False becomes 0. Similarly, when converting Booleans to strings, True becomes "True", and False becomes "False".
To convert a Boolean to an integer or string, you can use the int() and str() functions, respectively. Here's an example:
bool_value = True int_value = int(bool_value) # 1 str_value = str(bool_value) # "True"How can Python Booleans be Used to Write Efficient and Readable Code?
Booleans are a critical component in writing efficient and readable code in Python. They are often used in conditional statements and loops to control the code's flow based on specific conditions. Using Boolean expressions helps make your code more expressive and easy to understand.
For instance, instead of writing:
if len(some_list) > 0:
do_something()You can use the Boolean value directly:
if some_list:
do_something()The latter example is more Pythonic and easier to read. You can find more Python programming tips and best practices to improve your code readability and efficiency.
Is it Possible to Assign Values to True or False in Python?
In Python, True and False are keywords, and you cannot assign values to them directly. However, you can assign the True or False values to variables and use them in your code.
is_valid = True
is_active = FalseTrying to assign values directly to True or False will result in a SyntaxError. For example:
# This will raise a SyntaxError
True = 1To avoid this error, always use variables to store and manipulate Boolean values in your code.
Comparison Operators in Python
Comparison operators in Python are used to compare two values and return a Boolean result. These operators include:
==: Equals!=: Not equals<: Less than>: Greater than<=: Less than or equal to>=: Greater than or equal to
Using comparison operators is an essential part of Boolean testing in Python. For example, to check if two variables a and b are equal, you can use the == operator:
result = a == bThe result variable will hold the Boolean value True if a and b are equal, and False otherwise.
Python Boolean Functions
Python offers several built-in functions that work with Boolean values, such as all() and any(). These functions are useful in various scenarios when working with lists or other iterable data structures.
all(iterable): ReturnsTrueif all elements in the iterable areTrue, or the iterable is empty. Otherwise, it returnsFalse.any(iterable): ReturnsTrueif at least one element in the iterable isTrue. Otherwise, it returnsFalse.
Here's an example of how to use these functions:
numbers = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
is_all_odd = all(num % 2 == 1 for num in numbers)
is_any_even = any(num % 2 == 0 for num in numbers)In this example, is_all_odd will be True, as all numbers in the list are odd. is_any_even will be False, as none of the numbers are even.
Conclusion
Understanding and using Python Boolean functions effectively can help you write more efficient and readable code. To learn more about Python Booleans and related topics, explore our Python tutorials and master the art of Python programming.